Be 7x More Effective at Identifying AI-Generated Responses in Language Assessments
SHL Labs study finds that more than 5% of candidates use ChatGPT in written language assessments and demonstrates the efficacy of SHL’s AI detection framework to automatically detect such cases.
Share
Large Language Models (LLMs) such as ChatGPT have rapidly evolved and mastered human-like writing abilities. As LLMs become more sophisticated and accessible, hiring managers and professors are faced with the considerable challenge of evaluating candidates’ and students’ writing abilities. The effectiveness of traditional, written language assessments in measuring argument framing, coherence, grammar, and vocabulary has been called into question due to the rise of generative AI models. These models can now handle many of these aspects with great accuracy, potentially allowing candidates to pass assessments by relying on AI-generated responses. From this blog, we will learn that:
- The use of ChatGPT in written language assessments has increased significantly in recent months, and traditional methods are not effective in detecting AI-generated responses.
- We found that candidates often make small variations (i.e., adding extra spaces) to ChatGPT-generated responses to avoid being flagged by detectors.
- SHL’s AI detection framework is highly effective in identifying candidates who are using ChatGPT (including any self-introduced variations) and provides 7x better accuracy to detect the use of AI-generated content.
According to our prior research, written language assessments are highly susceptible to AI-generated responses and candidates may use LLMs like ChatGPT to complete their assessments. One of the most notable weaknesses of LLMs is that they are overly predictive of the text that they generate and therefore, their output has a relatively high level of redundancy. Traditional methods have used textual pattern matching (i.e., repeated presence of phrases in source and target text) to detect copying from the internet and recently, they are extended to methods to detect ChatGPT-generated responses.
SHL’s AI detection framework uses textual pattern matching along with a custom-trained machine learning classifier. In our previous blog, we conducted a study to determine whether a statement was human-generated or not. On a database of 1 million language assessment essays, our machine learning classifier provided over 99% accuracy in distinguishing between AI-generated and human-written text.
We used our AI detection framework and conducted a comprehensive research study by analyzing over 160,000 language assessments (i.e., essays) from an English-language assessment between December 2022 and April 2023. While there are many openly available LLMs including paid and free ones, we focus our study on OpenAI’s GPT3.5/ChatGPT/GPT-4 language models due to their popularity and reach. Our study yielded several interesting insights, which are summarized below:
Insight 1: Our study has revealed 5% of candidates are using ChatGPT for clearing their language assessments. This has surged by 10X, post its launch indicating its growing significance and impact in the assessment industry. The number of candidates using ChatGPT in their assessments continues to increase month over month, with the highest ever recorded in April’23.
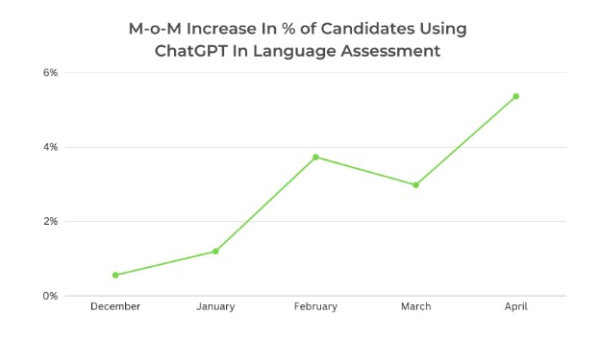
Our study has revealed that 5% of candidates are using ChatGPT for clearing their writing assessments. This has surged by 10X post its launch indicating its growing significance and impact in the assessment industry.
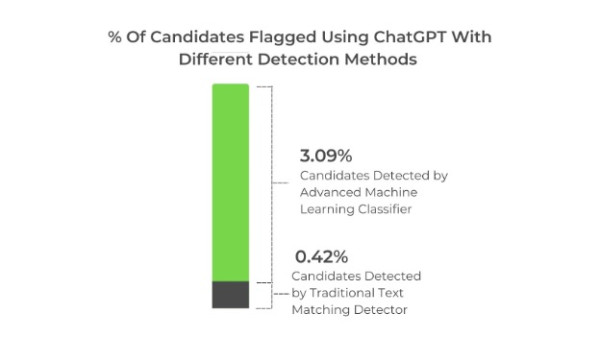
Insight 2: We found that traditional textual pattern-matching algorithms are not very effective in detecting responses by ChatGPT in language assessments. Our advanced machine learning classifier helps detect at least 7x more candidates who are using ChatGPT as compared to only textual pattern matching algorithms.
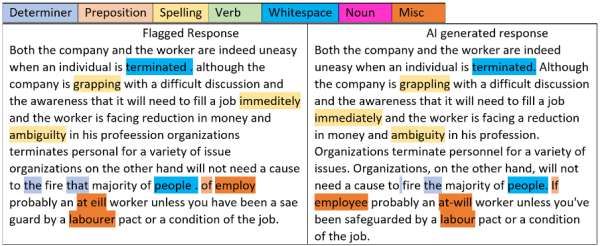
Insight 3: Our study discovered that candidates often make changes to AI-generated responses in their language assessments to avoid being flagged by an AI detector. One common tactic, demonstrated in the sample passage below, is to make changes in the text, such as adding an extra space after certain words like "terminated" or "people". This helps them evade detection by AI detectors.
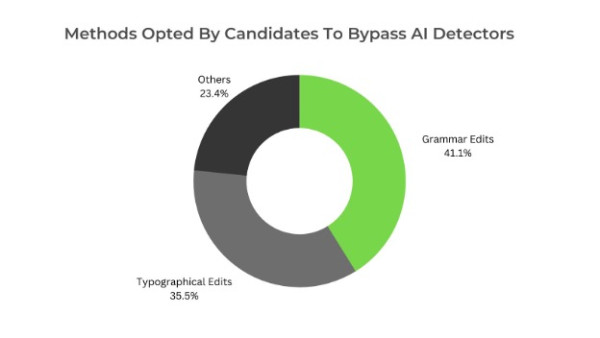
Insight 4: Our research study finds a comparatively high number of consciously introduced grammar errors by the candidates as compared to typographical (spelling, whitespaces, punctuation, etc.).
In summary, we have evaluated the actual influence of LLMs on the authenticity of essay evaluations in language assessments and showcased the effectiveness of SHL's robust framework for identifying instances of textual similarity. Additionally, SHL's Talent Central Platform uses deterministic and probabilistic proctoring signals to monitor candidates during assessments.
These signals can help detect if candidates are using ChatGPT or other AI tools to generate and copy-paste responses into the SHL assessment platform. As the technology landscape continues to evolve, SHL Labs is committed to staying at the forefront of emerging technologies and trends to provide guidance and insights in the field of talent assessment.
If you want to know more, please reach out to us.










